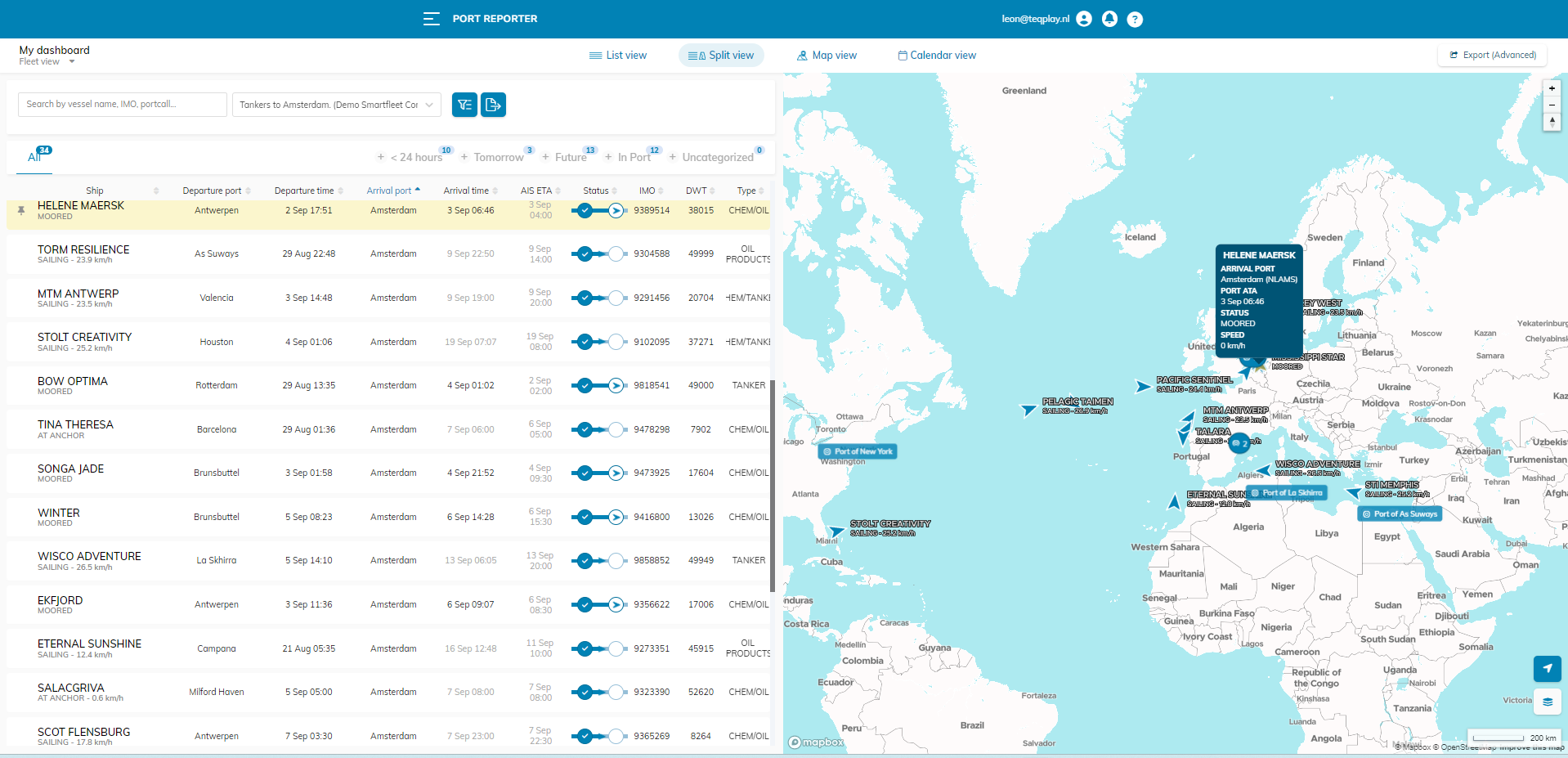
Dry bulk refers to the shipment of non-liquid or non-containerized cargo, such as grains, minerals, and construction materials, typically transported in large quantities. Dry bulk is a crucial component of the maritime supply chain, providing the transportation of essential goods such as raw materials, food, and construction materials to various parts of the world.
The dry bulk supply chain involves a complex network of participants, including stakeholders from shipping companies and port authorities. Each of these players plays a critical role in the process, and their interactions and collaboration must be seamless and efficient to ensure the smooth flow of goods.
Shipping Companies
Shipping companies provide the physical transportation of dry bulk commodities, operating a fleet of vessels that are designed to carry different types of dry bulk cargo. They are responsible for the safe and efficient transport of goods, and they play a critical role in the dry bulk supply chain.
Port Authorities
Port authorities manage the infrastructure and operations of ports, including the loading and unloading of dry bulk vessels. They are responsible for ensuring the efficient flow of cargo through their facilities, and they work closely with other participants in the supply chain to ensure a smooth and seamless experience for all parties involved.
Challenges and Opportunities
The dry bulk shipping industry is facing a number of challenges, including overcapacity, low freight rates, and increased regulatory scrutiny. However, the industry is also presented with a number of opportunities for growth, including the increasing demand for dry bulk commodities, particularly from emerging economies. Together with rising demand is the increasing need for more efficient and sustainable supply chain solutions.
- Overcapacity
Overcapacity is a significant challenge facing the dry bulk shipping industry, as the number of vessels available to transport goods exceeds the demand for their services. This has resulted in lower freight rates and reduced profits for shipping companies, making it difficult for them to invest in new technologies and maintain their fleets.
- Low freight rates
Low freight rates also impact the ability of shipping companies to invest in new technologies and innovations that could improve the efficiency and sustainability of their operations.
- Increased regulation
The dry bulk shipping industry is facing increased regulatory scrutiny, as governments around the world look to limit the environmental impact of the sector. This includes new emissions standards for vessels, stricter requirements for the disposal of waste materials, and increased pressure to reduce carbon emissions. Shipping companies must adapt to these new regulations while also maintaining their competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Despite these challenges, the dry bulk shipping industry is also presented with a number of opportunities for growth. One of the main opportunities is the increasing demand for dry bulk commodities, particularly as the world population continues to grow and economies continue to develop. This is especially true for emerging economies, which are driving much of the demand for raw materials and other goods.
The rising need for more efficient and sustainable supply chain solutions is also something that maritime businesses should pay attention to. As consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of their actions, they are demanding products that are produced and transported in a sustainable manner. Shipping companies that can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and efficiency will be better positioned to succeed in the long-term.
Technological Solutions
To address these challenges and capitalize on opportunities, the maritime industry has to adopt more innovative technological solutions. Digital transformation in the industry is on the rise, including the widespread adoption of digital solutions such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI).
One of the key benefits of the maritime digital transformation is improved data management. With the use of digital technologies, shipping companies can collect and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling them to make informed decisions about the movement of goods and the deployment of their fleets. This can lead to more efficient operations and lower costs, as well as greater transparency and improved supply chain visibility.
The increased use of automation is also a significant advantage. Automated systems can be used to optimize cargo management, vessel routing, and other key processes, helping shipping companies to reduce waste and improve their bottom line. For example, automated systems can be used to optimize vessel loading and unloading, reducing the time and resources required to complete these tasks.
Digital transformation is also helping the industry become more sustainable. Digital technologies can be used to monitor and reduce emissions from vessels, as well as to track and manage the waste generated by shipping operations. This not only helps shipping companies to meet regulatory requirements, but it also supports their efforts to be more environmentally responsible and to meet the growing demand for sustainable goods and services.

Léon Gommans | CEO/Co Founder of Teqplay
A serial entrepreneur who’s passionate about #innovation, #technology, #collaboration, and of course, #maritime. The mission is: to connect the dots & to get it to work, together with the industry!
- +31 (0)6 55306660
- leon@teqplay.com
- Léon Gommans